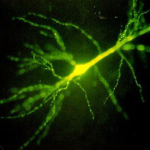
Microcircuit signatures of brain metastasis
In people suffering brain metastasis, cognitive impairment has been traditionally thought to result from the mass effect of the tumor growth. Recently, we teamed […]
Read MoreCell-type pro-sclerotic trajectories
Temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with hippocampal sclerosis, which is characterized by specific patterns of neuronal loss along hippocampal subfields from the CA1 to […]
Read MoreProximodistal organization of CA2
The proximodistal axis is considered a major organizational principle of the hippocampus. The CA2 region apparently breaks this rule. We discovered that CA2 is […]
Read MoreSublayer organization of CA1 replay
A major goal of my lab is understanding biological complexities. In the hippocampus, this manifests in terms of a variety of cell types and […]
Read MoreMechanisms of epileptic fast ripples
Fast ripples are high-frequency oscillations (HFOs) >250 Hz recorded in epileptogenic hippocampal regions. In 2007, we proposed a mechanism by which fast ripples emerge […]
Read MorePopulation activity thresholds
Generation of population activities such as hippocampal sharp wave ripples and epileptiform discharges follows an emergent dynamics. During my postdoc with Richard Miles, we […]
Read MoreUbiquity of immature population bursts
The idea of a critical period in hippocampal postnatal development characterized by hyperexcitability was a major research line in the 90s. Giant Depolarizing Potentials […]
Read More